You did not elect a section 179 deduction and the property is not qualified property for purposes of claiming a special depreciation allowance, so your property’s unadjusted basis is its cost, $10,000. You use GDS and the half-year convention to figure your depreciation. You refer to the MACRS Percentage Table Guide in Appendix A and find that you should use Table A-1. Multiply your property’s unadjusted basis each year by the percentage for 7-year property given in Table A-1.
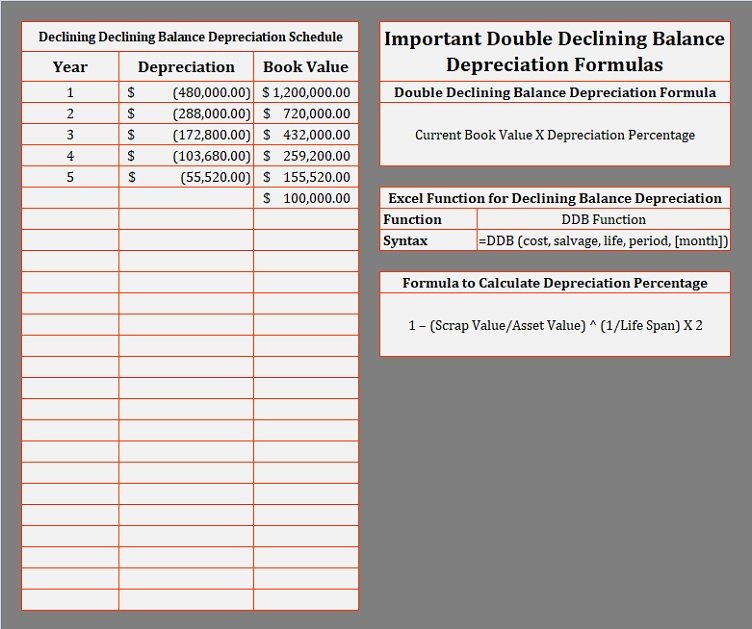
What is Double Declining Balance Depreciation?

You must allocate the dollar limit (after any reduction) between you equally, unless you both elect a different allocation. If the percentages elected by each of you do not total 100%, 50% will be allocated to each of you. You must continue to use the same depreciation method as the transferor and figure depreciation as if the transfer had not occurred. However, if MACRS would otherwise apply, you can use it to depreciate the part of the property’s basis that exceeds the carried-over basis. You can include participations and residuals in the adjusted basis of the property for purposes of computing your depreciation deduction under the income forecast method.
Declining Balance Method of Assets Depreciation FAQs
The nontaxable transfers covered by this rule include the following. You cannot use MACRS for personal property (section 1245 property) in any of the following situations. For a discussion of when property is placed in service, see When Does Depreciation Begin and End, earlier. For a description of related persons, see Related Persons, later.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
If there are no adjustments to the basis of the property other than depreciation, your depreciation deduction for each subsequent year of the recovery period will be as follows. In July 2023, the property was vandalized and they had a deductible casualty loss of $3,000. Sandra and Frank must adjust the property’s basis for the casualty loss, so they can no longer use the percentage tables.
If you transferred either all of the property, the last item of property, or the remaining portion of the last item of property, in a GAA, the recipient’s basis in the property is the result of the following. To make it easier to figure MACRS depreciation, you can group separate properties into one or more general asset accounts (GAAs). You can then depreciate all the properties in each account as a single item of property.
Calculation of the Declining Balance Depreciation Rate
- You generally cannot use MACRS for real property (section 1250 property) in any of the following situations.
- Sandra and Frank must adjust the property’s basis for the casualty loss, so they can no longer use the percentage tables.
- This means that, for a 12-month tax year, 1½ months of depreciation is allowed for the quarter the property is placed in service or disposed of.
- You use the remaining cost of the property to figure a regular MACRS depreciation deduction for your property for 2023 and later years.
- In other words, it records how the value of an asset declines over time.
If you want to learn more about fixed asset accounting as a whole, then head to our guide on what fixed asset accounting is, where we discuss the four important things you need to know. Also, if you want to know the other essential bookkeeping tasks aside from fixed asset accounting, you can read our piece on what bookkeeping is and what a bookkeeper does. If the beginning book value is equal (or almost equal) with the salvage value, don’t apply the DDB rate. Instead, compute the difference between the beginning book value and salvage value to compute the depreciation expense. Using the rate from the calculation above, the declining balance depreciation for each of the 4 years is as follows. Reducing balance method causes reported profits of a company to decline by a higher depreciation charge in the early years of an assets life.
The use of your own automobile or a rental automobile is for the convenience of Uplift and is required as a condition of employment. In May 2023, Sankofa sells its entire manufacturing plant in New Jersey to an unrelated person. The sales proceeds allocated to each of the three machines at the New Jersey plant is $5,000. This transaction is a qualifying disposition, so Sankofa chooses to remove the three machines from the GAA and figure the gain, loss, or other deduction by taking into account their adjusted bases. When you dispose of property included in a GAA, the following rules generally apply. The DB method provides a larger deduction, so you deduct the $192 figured under the 200% DB method.
Step 1—Taxable income figured without either deduction is $1,180,000. Under certain circumstances, the general dollar limits on the section 179 deduction may be reduced or increased or there may be a sample profit and loss statement to help your business additional dollar limits. The general dollar limit is affected by any of the following situations. Only the portion of the new oven’s basis paid by cash qualifies for the section 179 deduction.
